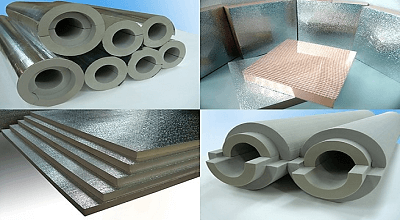
Hot Insulation
When ever operating temperature is higher than the ambient temperature and heat lose occurs during the process, Hot Insulation shall be applied. Material used in hot insulation must have high melting point to resist temperature. Temperature may vary from 50 degrees to 1500 degrees.
- Thermocole ( Expanded Polystyrene foam) Insulation Commonly know as EPS
- Polyurethane Foam ( Puff Insulation )
- Chemically Cross link Polyethylene Commonly known as XLPE
- Elostromeric Nitrile Rubber Insulation
- Perlite Rigid Insulation
- Thermo isolate
- Humidity
- Wind Velocity
- Material Structure
- Thermal Conductivity
- Water vapor permeability coefficient
- Due point temperature
Cold Insulation
Primary goal of Insulation is to Conserve energy , to maintain process temperature and to avoid condensation in context to reduce operating cost of any process. Simultaneously it also helps to reduce noise, for fire safety and personal Protection.
During cold insulation as ambient temperature is higher than the surface temperature than moisture in air condenses on surface To avoid condensation surface must be insulated with appropriate Insulation material with sufficient thickness and protected by vapour barrier. If Insulation system is not appropriate it will cause service life and performance, Corrosion of pipes, vessel and fitting within the insulation and cause water related damages to the machinery.
- Thermocole ( Expanded Polystyrene foam) Insulation Commonly know as EPS
- Polyurethane Foam ( Puff Insulation )
- Chemically Cross link Polyethylene Commonly known as XLPE
- Elostromeric Nitrile Rubber Insulation
- Perlite Rigid Insulation
- Thermo isolate
- Humidity
- Wind Velocity
- Material Structure
- Thermal Conductivity
- Water vapor permeability coefficient
- Due point temperature